Optimized components using the injection compression molding process
ESPAECIALLY FOR OUR USERS
If you are looking for a process with which you can produce high-precision or very large or even thick-walled plastic components, injection compression molding is a reliable process. The Moldex3D special module ICM (Injection Compression Molding) enables to simulate the injection compression molding process. The combination of injection molding and extrusion allows to combine the advantages of both processes.
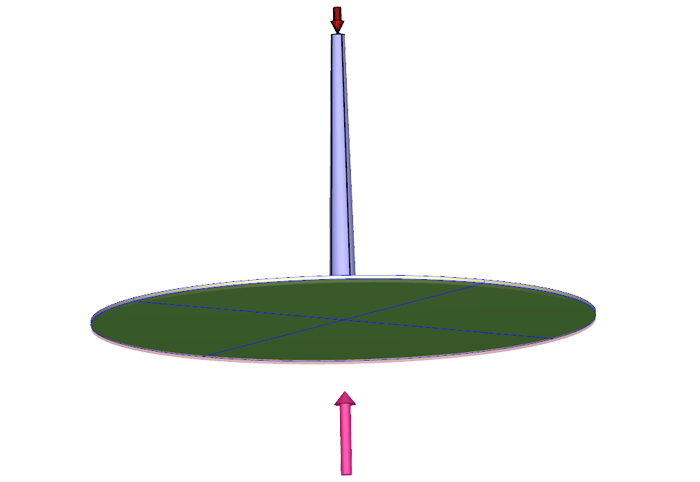
Injection compression moulding is a further development of injection molding and can be used on almost all machines. The plastic melt is injected as a so-called mass cake into the practically pressureless, not completely closed mold. It is only completely closed during the solidification process. The closing pressure that builds up evenly as a result ensures that the moulded part is finally formed.
The melt is usually injected into the cavity that is enlarged by the compression gap. Before this cavity is completely filled, the compression gap is closed and the residual filling is achieved. The embossing pressure can be applied evenly across the entire joint face or only partially. In Moldex3D, the embossing surfaces can be freely defined and thus the desired embossing behavior can be reproduced.
The residual filling via the embossing stroke offers a number of advantages, such as uniform shrinkage compensation and reduced internal stresses. However, the combination of injection and stamping process also leads to a more complex process control. This also results in more parameters in the simulation with Moldex3D, which influence the simulation result. In addition to the time of filling and temperatures, the height of the stamping stroke, the time of switching to the stamping process, stamping speeds and stamping forces must now also be considered.
Interested?! Please contact us at 0241 565 276-0 or send an email to info@simpatec.com.